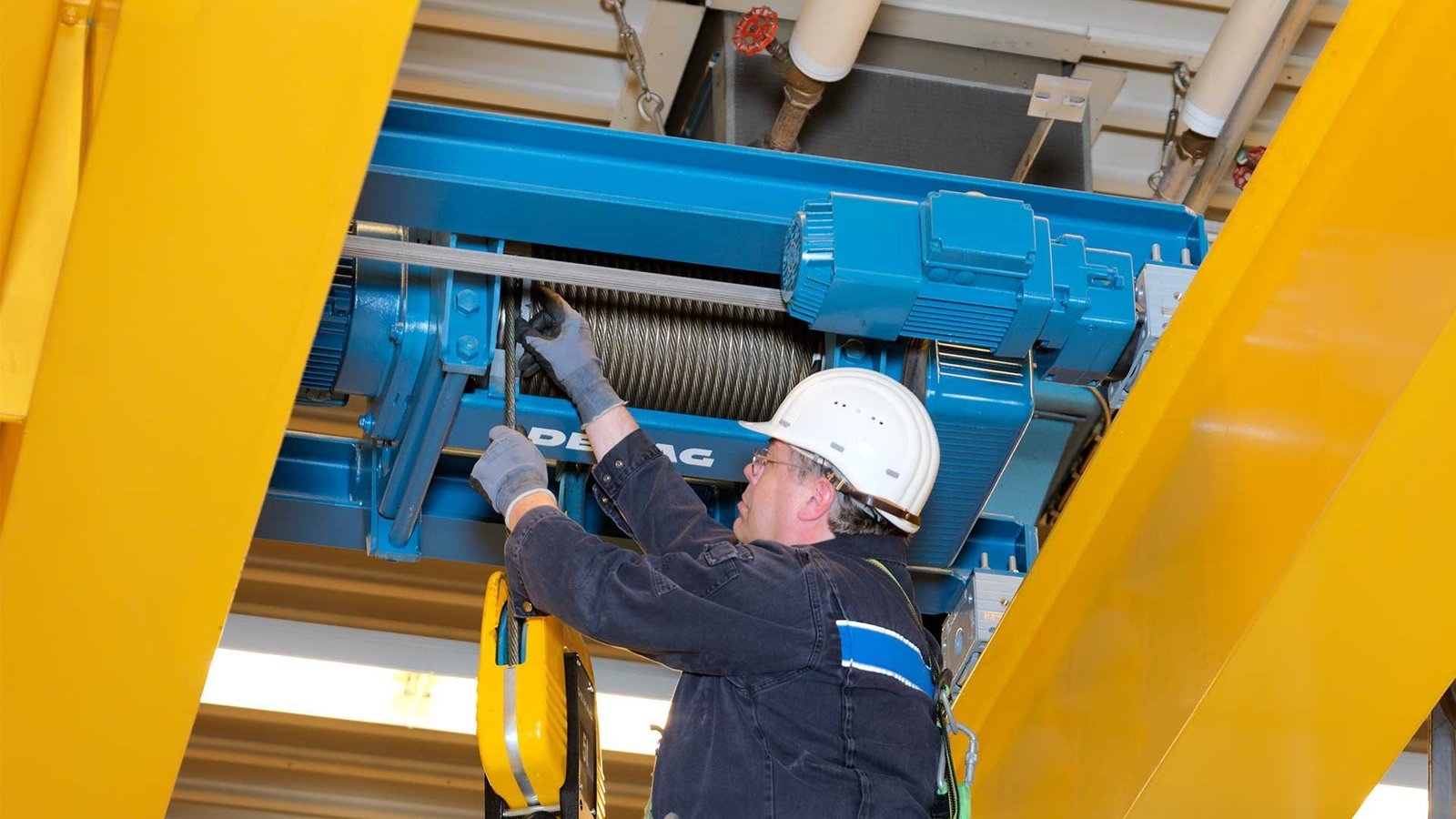

Services
Modifications & Retrofitting
Modifications and Retrofitting of cranes are processes aimed at enhancing the functionality, safety, or lifespan of existing crane equipment. Think of it like renovating an old house. Just as you might update the plumbing, wiring, or structure to improve safety, efficiency, or adapt to modern standards, modifying or retrofitting a crane involves upgrading or replacing key components to meet new requirements, improve performance, or extend its operational life.
Modifications and retrofitting are common practices used to improve or extend the life and functionality of cranes.
Cranes and Modifications
Modifications are changes or upgrades made to the crane’s existing systems to improve its performance, adapt to new challenges, or increase its capacity. This might be in response to changing job requirements, increased load demands, or regulatory changes.
Examples of Crane Modifications
- ncreased Load Capacity: Just as you might strengthen the foundation of a building to support heavier walls, cranes can be modified to lift heavier loads. This could involve reinforcing the crane’s structure, adding counterweights, or upgrading the hoisting system.
- Boom Extensions: Imagine adding more space to a house by extending its roofline. In a crane, this could mean adding an extension to the boom to increase reach, allowing the crane to lift loads further or to higher heights.
- New Lifting Mechanisms: Similar to upgrading kitchen appliances in a house to make cooking easier, cranes might be fitted with more advanced winches, pulleys, or hydraulic systems that make lifting faster or more efficient.
Cranes and Retrofitting
Retrofitting is the process of adding new features or systems to a crane that were not part of the original design. It’s like upgrading an old car with modern technology—adding a new navigation system, better brakes, or more fuel-efficient parts without replacing the entire vehicle.
Examples of Crane Retrofitting
- Adding Safety Features: Just as you might install modern security systems (like cameras or alarms) in an older house, retrofitting a crane might involve adding new safety features, such as load moment indicators, overload protection, or updated emergency shutdown systems to meet current safety standards.
- Upgrading Electrical Systems: Older cranes might have outdated electrical systems. Retrofitting these systems with modern wiring, sensors, or automated controls can improve reliability, reduce energy consumption, and make the crane easier to operate, much like installing energy-efficient lighting or smart thermostats in a home.
- Improving Stability: Think of this like reinforcing the walls of a building to make it earthquake-resistant. Cranes might be retrofitted with additional outriggers, upgraded stabilizers, or new undercarriage components to improve balance and stability, especially when working on uneven ground or lifting heavy loads.
Why Modify or Retrofit Cranes?
- Cost-Effective Solution: Instead of buying a completely new crane, modifications or retrofits allow you to “update” your crane and make it fit for purpose, often at a fraction of the cost of buying new equipment. It’s like updating a room in your house instead of building a whole new house.
- Extended Lifespan: Just like restoring an old building to make it last longer, retrofitting can extend the useful life of a crane. It addresses any outdated systems and ensures that the crane continues to operate efficiently and safely for many more years.
- Compliance with New Standards: Regulations change, and just as homes need to meet modern building codes, cranes must adhere to updated safety and operational standards. Retrofitting ensures the crane is up-to-date with current laws and operational practices, keeping it safe for use.
The Process of Crane Modifications and Retrofitting
Step 1: Assessment of Current Equipment Before making any modifications or retrofits, a thorough inspection of the crane is needed to determine its condition. Think of this as a contractor assessing the state of a building before beginning renovations. The goal is to identify what needs to be upgraded, replaced, or fixed.
Step 2: Design and Planning Once the assessment is done, a custom solution is designed based on the crane’s intended use and the specific requirements. This is akin to designing a floor plan for a renovation, deciding which changes will improve functionality and safety.
Step 3: Implementation The actual modifications or retrofitting is where the work happens. New components are added, old systems are replaced, and upgrades are installed. This process might take place at the crane’s current location or at a dedicated service center, depending on the complexity.
Step 4: Testing and Certification Once modifications or retrofitting is complete, the crane undergoes testing to ensure that the changes work as intended. This is similar to a final inspection after a home renovation, where inspectors ensure that everything meets code and safety standards.
Common Benefits of Modifications and Retrofitting
- Improved Performance: Just like upgrading a kitchen or installing a new air conditioning system in a house, modifications and retrofitting can dramatically improve the crane’s performance—making it faster, more efficient, or more capable of handling heavier loads.
- Increased Safety: Adding modern safety systems or retrofitting structural components can help prevent accidents, much like adding fire alarms or reinforcing a house against storms. A safer crane is less likely to cause injury or damage, benefiting both the crew and the equipment.
- Better Efficiency: Modernizing a crane can help it operate more smoothly and reduce downtime. This is like adding energy-efficient windows to a home—you get more out of the system for less effort.
